Why More Countries and Businesses Will Continue to Adopt Bitcoin
Game theory predicts that owning bitcoin is not a question of "if", but "when".
Introduction
Part of the reason why Bitcoin is hard to understand because it is interdisciplinary. Bitcoin cuts through economics, technology, and psychology.
My previous articles have focused more on economics and technology, so let’s talk about bitcoin from a psychology aspect this time around.
We know that psychology is a powerful force in predicting human behavior, especially in market behaviour and business decisions.
Game theory is a popular tool that predicts human behavior. It suggests that the question isn't whether the world will adopt bitcoin, but a matter of when.
Lets dive into why this is the likely case in four sections:
Introduction to Game Theory (Business Decisions, Nuclear Weapons)
Game Theory in Bitcoin Adoption
How is The Bitcoin Game Theory Adoption Theory Playing Out?
What This Means For You
1. Introduction to Game Theory (Business Decisions, Nuclear Weapons)
Game theory in short, is:
A mathematical framework
used to predict the behaviour of other people
in situations where your success depends on your actions AND the actions of others.
It is a powerful framework used in many areas including politics and business, and much of it relies on predicting human behaviours, hence the psychology aspect.
Business Example
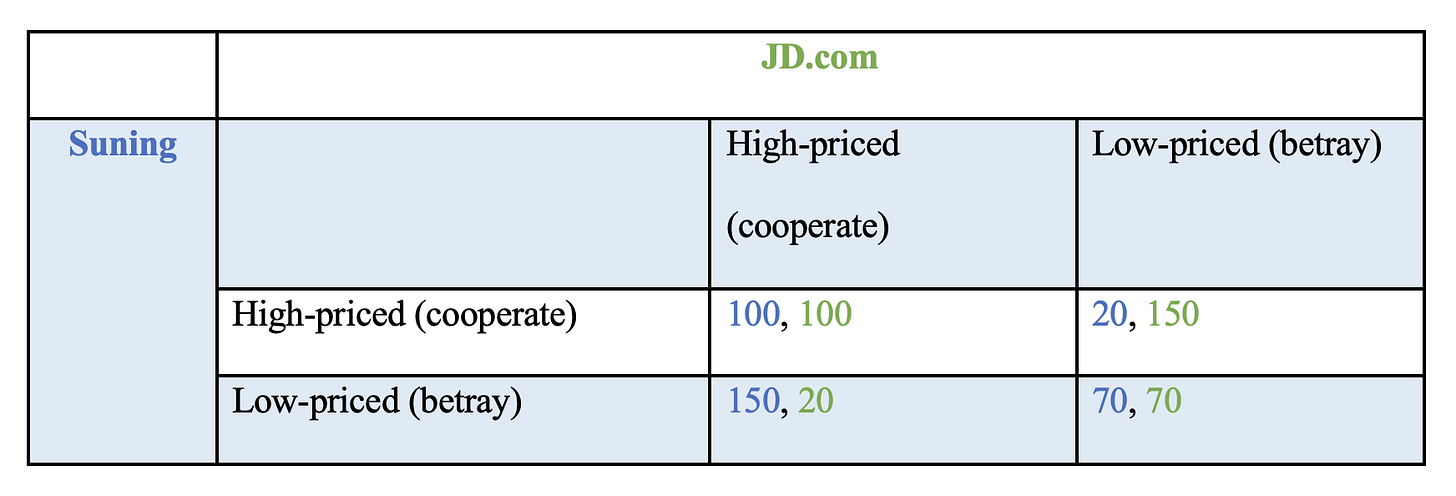
The example below from Cornell University shows how two companies (JD and Suning) need to make a decision on whether to make their service high-priced (expensive) or low-priced (cheap). Assume that they do not have a chance to communicate about pricing beforehand due to legal implications, and that the numbers are in million dollars
One way to read the table above is by focusing on Suning and reading from left to right:
Suning’s possible outcomes are shown in blue.
If Suning chooses high-priced, it will either get $100 million (if JD also chooses high-priced) OR $20 million (if JD chooses low price)
If Suning chooses low-priced, it will either get $150 million (if JD chooses high-priced) OR $70 million (if JD also chooses low-priced)
Suning’s outcome not only depends on its decision, but also JD’s decision.
Even though the ideal scenario is for them to cooperate and set a high price together, notice that there is a large incentive to betray the other company to get the $150 million. Maybe one company wants to bet that the other cannot afford to lower its price, or maybe it just decides to try and get more market share.
Even if both start with high prices, all it takes is for one company to lower prices one time before the other one has to lower its prices.
Either way, game theory predicts that the most likely outcome is both companies choose to set a low-price on a permanent basis (which is what happened in real life).
If they somehow legally agreed to raise high prices together, you have what we call a cartel. Cartels are bad for consumers because consumers are generally forced to pay higher prices.
A well known example of a cartel is OPEC, which collectively agree to control oil production level to regulate prices. However, even cartels have been shown to struggle with members who do not follow production cuts.
Again, game theory explains why some OPEC members may choose to not cut: they simply get more money if others are cutting production but they are continuing to sell the same amount.
Politics Example
The other darker but important example is game theory in war. Specifically, nuclear weapons.
I won’t go into all the details here; Howstuffworks offers an easy-to-understand article on this specific topic without getting too technical.
The outcome of game theory in nuclear war is similar to the example above: first assume two countries are opponents considering whether they need nuclear weapons.
Even though the ideal outcome is for both countries to not have nuclear weapons (assuring world peace, saving cost etc.), it is more sensible for one country to prepare nuclear weapons in case the other country chooses to “betray” by also preparing its own nuclear weapon. Or else, you are leaving yourself unguarded and at risk of being attacked.
The end result is both countries possessing nuclear weapons.
To wrap up this section: game theory is widely studied, analyzed, adopted, and can be used to predict how other people will react to certain situations, given a fixed set of choices. Now, lets move on the bitcoin.
2. Game Theory in Bitcoin Adoption
While there is an aspect of game theory for bitcoin related to bitcoin mining and Bitcoin’s network, those are more technical and beyond the scope of this article.
Instead, we are focusing on the psychology of bitcoin adoption using a similar framework as we described above.
Furthermore, we are not just talking about you or me as individual investors.
We are talking about big players like countries, financial institutions, sovereign wealth funds.
Entities with billions of dollars at their disposal.
So what does game theory predict for bitcoin adoption? River, a U.S. based Bitcoin-only platform, has created a short video hinting at how this might work for countries.
Lets say two countries are considering whether to adopt bitcoin as part of their reserves.
If all countries do not adopt bitcoin, bitcoin may never gain country/government adoption (not retail or individual adoption, that is different), and the price of bitcoin in fiat terms might be dampened slightly.
However, if one country starts to adopt bitcoin, it forces other countries to reconsider their option.
If bitcoin’s demand continue to increase (and price of bitcoin increases as well) as more countries start to adopt it, then other countries have no choice but to adopt it eventually, as the later you adopt it, the greater your disadvantage (bitcoin will be even more scarce and expensive).
Note that adopting bitcoin as a reserve means directly or indirectly accumulating bitcoin, or having some form of official approval or statement that bitcoin is part of the country’s reserves. Simply having bitcoin from past events (e.g. confiscating bitcoin) does not count.
The same works for financial institutions, but for slightly different reasons. For example, if an established institution starts to offer bitcoin investment products, others are then forced to consider offering it, or else they may potentially lose customers.
For businesses, it works similarly to countries. Businesses that adopt bitcoin will likely gain a significant financial advantage over the long term as bitcoin is one of the best performing assets and a reliable form of savings.
In short, as more and more entities start to adopt bitcoin, others will have no choice but to consider and eventually adopt it.
And the number of adopters will only continue to increase as more people spend time to learn and understand bitcoin. More importantly, once someone truly understands bitcoin, they will not turn from it ever again because it is technologically and economically a superior form of money.
3. How is The Bitcoin Game Theory Adoption Theory Playing Out?
Firstly, it may help to zoom out and look at bitcoin’s overall journey since 2008 and where we are at:
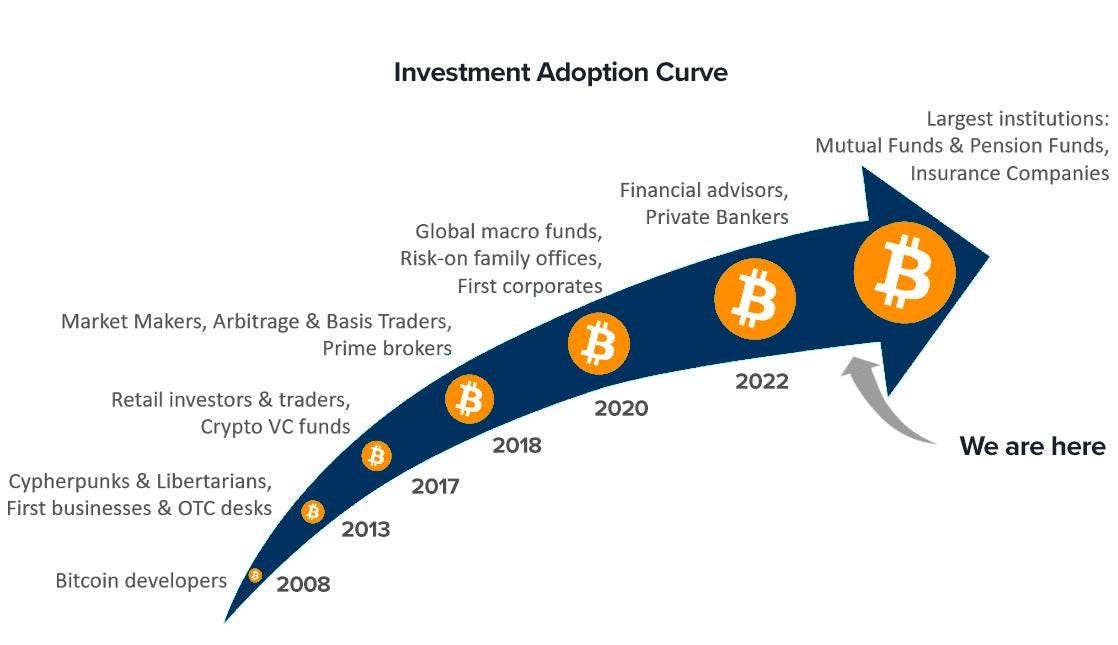
What happened during 2020-2024? Paraphrasing Swan Bitcoin below:
In the early 2020s, corporations like MicroStrategy and Tesla announced treasury strategies to acquire and hold Bitcoin on their balance sheets.
In 2021, El Salvador transformed their country by adopting Bitcoin as legal tender and setting Bitcoin-friendly policies to drive growth.
In January 2024, the likes of BlackRock, Fidelity, and the biggest asset managers on the planet entered the Bitcoin network through the approval of the first spot Bitcoin ETFs.
El Salvador has been buying 1 bitcoin consistently everyday, including weekends.
A lot more happened in the last four years among countries and non-crypto institutions that was not mentioned above. For example,
the world’s first Bitcoin Spot ETF was launched in Canada’s Toronto Stock Exchange in February 2021
Australia also launched its first Bitcoin ETF in May 2022, followed by a second one in July 2024
Japan’s finance corporation Metaplanet officially adopted bitcoin as its reserve asset in April 2024 to “mitigate risks associated with Japan's massive debt burden and the yen volatility”
US State Pension funds like the Wisconsin Pension Funds and Michigan Pension Funds have started accumulating bitcoin in mid-2024
Bitcoin’s institutional adoption has been on a global scale since 2020, and the trend is only moving in one direction: more adoption
It is important to note that while many crypto companies hold bitcoin (mostly exchanges or bitcoin miners), the key difference here is that non-crypto companies are now holding bitcoin as a reserve assets.
This means they do not intend to deploy or sell bitcoin unless absolutely necessary, like during periods of crisis. For example, refer to how Singapore has deployed its reserve assets only once during the 2008 financial crisis and four times the COVID-19 crisis.
In summary, the game theory of Bitcoin adoption is already unfolding across different sectors. Wealth funds, countries, and businesses are all beginning to recognize the potential advantages of adopting Bitcoin early. As more players enter the game, the pressure on others to do the same will only increase, driving further adoption and solidifying Bitcoin's place in the global economy.
4. What This Means for You
Whether you are an individual investor or a business owner, you should be looking to protect and grow your capital. Bitcoin is one of the best ways to do that, but it requires you to understand what makes money, money, in the first place, before you can commit to bitcoin.
Fundamentally, bitcoin is a technologically better, more robust form of money, not subject to human manipulation. The easiest way to think about it is that it’s a superior version of gold.
There are plenty of resources out there on the internet to learn about bitcoin, but it can be difficult and time-consuming to synthesize the information by yourself. Hence, my friend and I have made it our mission to help others understand and adopt bitcoin. We founded Fortis Bitcoin, a bitcoin-only advisory firm to understand bitcoin, and guide you on how to secure and protect your bitcoin. We condense over 2,000 hours of self learnings into 2-hour sessions to help you understand bitcoin. We also help you set up, buy and protect your bitcoin.
Closing thoughts
Institutions and countries adopting bitcoin are doing so with a year or decade horizon in mind. As an individual investor, understanding this long-term perspective can help you stay focused on the bigger picture rather than getting caught up in short-term market fluctuations.
If game theory is any indication, Bitcoin adoption among major entities will likely continue to grow. This shift is inevitable and bitcoin will become even more scarce as more people continue to buy and hold bitcoin as their reserve assets.
A good rule of thumb on practical next steps would be:
Understand bitcoin’s value proposition
Understand your own financial goals
Understand both the short-term risks and rewards of bitcoin
When you decide to commit to bitcoin, reach out to someone reliable to get onboarded.
Remember: the question to ask for bitcoin is not “if” we will adopt it, but “when”.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this publication is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Readers are encouraged to do their own research and consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions.